
Obstructions in your middle ear or blockages in your ear canal can cause damage to your auditory system and other problems like tinnitus. These blockages build up pressure in the inner ear and disrupt the functions of the eardrum. Some of the typical ear blockages that we experience are caused by
- Excessive ear wax (also known as ceruminosis)
- Dirt or foreign objects
- Loose hair from the ear canal
- Middle ear infections
Here's what you need to know. Our body produces earwax to trap specks of dirt and protect our ears. However, excessive earwax can trigger tinnitus and have far-reaching effects.
Tinnitus is a debilitating neurological and audiological condition that affects more than 50 million Americans. Patients typically hear persistent ringing and buzzing sounds in their ears and head. A variety of underlying health conditions mostly causes the disease.
For some patients, their tinnitus may be due to age-related and noise-induced hearing loss. Other patients may experience tinnitus due to head and neck injuries, exposure to loud sounds, whiplash, earwax, etc.
More often than not, tinnitus caused by earwax blockages is overlooked. In many cases, removing the ear wax blockage may alleviate tinnitus symptoms. Albeit, in some situations, the blockage may have caused permanent damage that leads to chronic tinnitus.
So, if you just started hearing persistent ringing in your ears, your tinnitus may be caused by earwax blockage. In this article, we will proffer solutions to help you prevent or treat your condition.
Alright, let's get to it.
What is Earwax?

Our body naturally produces a lot of substances, and earwax is one of them. Earwax (also known as Cerumen) is a waxy substance secreted by the body to protect our ears from infections. Research has shown that earwax contains
- Six to nine percent of cholesterol
- 60 percent of Keratin
- About 12 to 20 percent of alcohol
- Saturated and unsaturated long-chain fatty acids
Practically, everyone has earwax. Albeit, the composition may differ from person to person and also depends on their age, environment, ethnicity, and diet.
Earwax is primarily made up of shed layers of skin and produced by sebaceous glands in the outer part of our ear. As the ear canal's skin grows from inside out, motions that occur when we chew and other jaw movements cause the old ear wax to move through the ear canal. After a long time, the wax reaches the outside of the ear and flakes off.
Research has shown that earwax is slightly acidic and also has lubricative and antibacterial properties. Although earwax looks gross, dirty, and repulsive, you need a considerable amount of earwax to stay healthy.
Without earwax, our ear canal would become dry, waterlogged, and prone to infection. That's why a good batch of earwax should include oil and sweat mixed with dead skin cells and dirt.

Yes, I get it. It's tough to believe that something so unappealing, sticky, smelly, and sometimes itchy can be very critical to your ears' good health.
Benefits of Earwax
Let's take a look at why you need some earwax.
- Earwax acts as a natural barrier that prevents bacteria, dirt, and other dangerous debris from entering your ear. Due to its sticky and oily nature, it efficiently traps microscopic debris that finds its way into your ear canal. Without this protective barrier, your ear would be at risk.
- Earwax forms a protective coating for your ear canal and also acts as a moisturizer. Without this sticky substance, your ears may become itchy and flaky, thereby exposing you to a higher risk of irritation and infection.
- Insects and bugs do not like the smell of earwax, so it acts as an insect repellant. The sticky nature of earwax also traps the insects that accidentally fall into your ear.
Excessive Earwax and Tinnitus

Your ears are self-cleaning, so earwax should find its way out of your ear naturally when they dry up. However, while this process normally happens for some people and without problems, others experience earwax blockages or impaction.
Earwax blockage or impaction occurs when earwax (cerumen) piles up or accumulates in your ear to the point where it becomes too hard to wash away or fall away naturally.
Blockages typically happen when you use items like cotton swabs, earbuds, or bobby pins to clean your ears over some time. These items end up pushing the earwax farther into the ears, thereby causing injury and impaction.
Sometimes, impaction may happen because your ear is secreting excessive amounts of wax. Also, people that produce dry cerumen might experience buildup more often.
In many cases, excessive amounts of earwax can trigger tinnitus, a debilitating condition characterized by persistent ringing and buzzing in the ears. Tinnitus negatively impacts a patient's overall health and social well-being. Patients often experience depression, anxiety, irritability, and lack of concentration.
If you've been living with tinnitus, it's best to visit your audiologists to check if an earwax blockage or impaction causes your condition.
The good news is that removing earwax or blockages may provide relief and alleviate temporary tinnitus symptoms. However, in severe cases, the impaction may damage the auditory system and cause permanent and chronic tinnitus.

Here are other symptoms you may experience due to earwax impaction
- Pain in the affected ear
- A feeling of fullness in the ear
- Hearing difficulty (which may worsen over time)
- Humming, buzzing noise, or ringing in the ear or head (tinnitus)
- Itchiness in the ear
- Discharge and foul order from the affected ear
- Cough
- Dizziness and nausea
If you experience any of the earwax blockage symptoms we've listed above, don't attempt to remove the earwax on your own. Talk to your doctor.
You may think you can deal with the earwax by merely using items like earbuds. But there's no better way to know if you have excessive earwax buildup without having your doctor look in your ears.
Moreover, having those symptoms doesn't necessarily mean you have excessive earwax buildup or impaction. The signs may be associated with another health condition. For instance, pain in the ear may be a result of head or ear trauma. The tinnitus-like sounds may be due to short or long-term exposure to noise or as a result of ototoxic medications.
So your doctor is in the best position to diagnose your condition and recommend the best treatment option properly.
Treatment of Tinnitus caused by Excessive Earwax
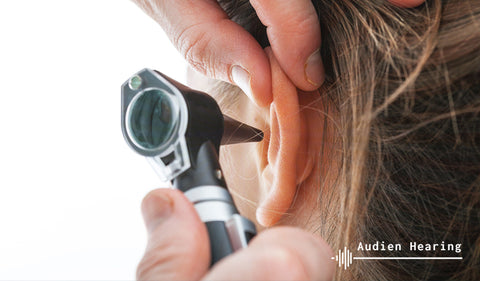
If your tinnitus is induced by excessive earwax, loose hair, or a foreign object, earwax removal by a qualified health professional will cause your tinnitus to go away.
Let's take a look at some of the recommended earwax removal tips.
Medical Diagnosis and Treatment
Like we mentioned earlier, earwax is supposed to fall off on its own. So If your ear impaction symptoms are severe, you should visit your doctor.
Your doctor will examine your ear using a unique medical instrument called an auriscope or otoscope. This device magnifies and lights up your ear and enables your doctor to spot ear blockage, infections, and other illnesses.
Depending on your condition, your doctor may use one or more treatment methods to cure your tinnitus. Here are some of the widely accepted treatment options.
Ear Irrigation

Ear irrigation involves applying high-pressure water from rubber-bulb syringes or water pick to the ear canal to flush and dislodge the earwax. The flow of water into the ear may tingle or feel strange but certainly not painful.
Today, medical health professionals use electronic ear irrigators to ensure that the squirt or water flow into the ear is controlled at body temperature and normal pressure.
It's important to note that irrigation is not suitable for all patients. For example, patients that have had ear surgery in the last 12 months should not undergo this procedure. Also, individuals with perforated eardrums or illnesses like infections of the middle ear or severe earache should not experience irrigation.
Use of Eardrops
Applying ear drops can also soften the wax within a few days and make it easier to come out. Ear drops can irritate the delicate skin of your ear canal or eardrums. That's why you should only use ear drops that are recommended by a medical doctor.
Your doctor may also recommend the use of wax-removal medication, like
- Carbamide peroxide
- Murine Ear Wax Removal
- Debrox
- Mollifene etc.
Manual Removal of Excessive Earwax

If irrigation or applying ear drops doesn't solve the issues, your doctor may need to remove the excess wax by microsuction. During this procedure, doctors use a small and curved instrument called a curet to suck earwax out of the ear canal and clean the ear. Other tools like hooks, spoons, and courgettes are used to perform this procedure.
Home Remedies for Excess Earwax Removal
It's common to find people pushing objects like earbuds and cotton swabs into their ears in a bid to remove dirt.
Be warned. This action can result in severe earache, ear infection, and damage to your auditory system.
If you cannot get medical help, there are recommended home remedies that will help you eliminate earwax impaction.
One of the most effective methods is cleaning the outer ear with a warm and wet towel. This cleaning method softens the earwax and causes it to fall out. However, you may need to repeat this process a few times to experience relief.

Another effective DIY remedy is by applying a few drops of ointments and eardrop to your ear canal. You can quickly get mineral oils, glycerin, olive oil, baby oil, almond oils from any pharmaceutical store close to you.
To apply the ear drops effectively, tilt your head so that your ear faces upwards. Go ahead and place one or two drops in it, and wait for 1–2 minutes before allowing the liquid to drain out. If you keep at it for two weeks or more, the earwax will soften and fall out of your ears.
You can also use the irrigation method at home. With a rubber-bulb syringe, gently squirt warm water into your ear. Just like the eardrop, the warm water helps to soften the earwax. And after some days, the earwax will fall out gradually.
If you still experience tinnitus after earwax removal, you need to undergo further diagnosis and tests to discover the cause of your tinnitus and effective treatment options.
Unfortunately, permanent tinnitus does not have a cure. The good news is that current treatment options will help you cope with the condition.
Summary
Although earwax lubricates, cleans, and protects the ear canal, excessive earwax can trigger tinnitus-like sounds in your ear.
The thing is, tinnitus symptoms are not exclusive to patients with ear blockages only. It is also associated with various underlying medical conditions, including head or neck trauma, ototoxic medications, etc. However, if your tinnitus is caused by excessive earwax or impaction, removing these blockages will make your tinnitus go away.
Please consult a qualified medical health professional for proper diagnosis and treatment if you experience tinnitus or earwax impaction symptoms.













